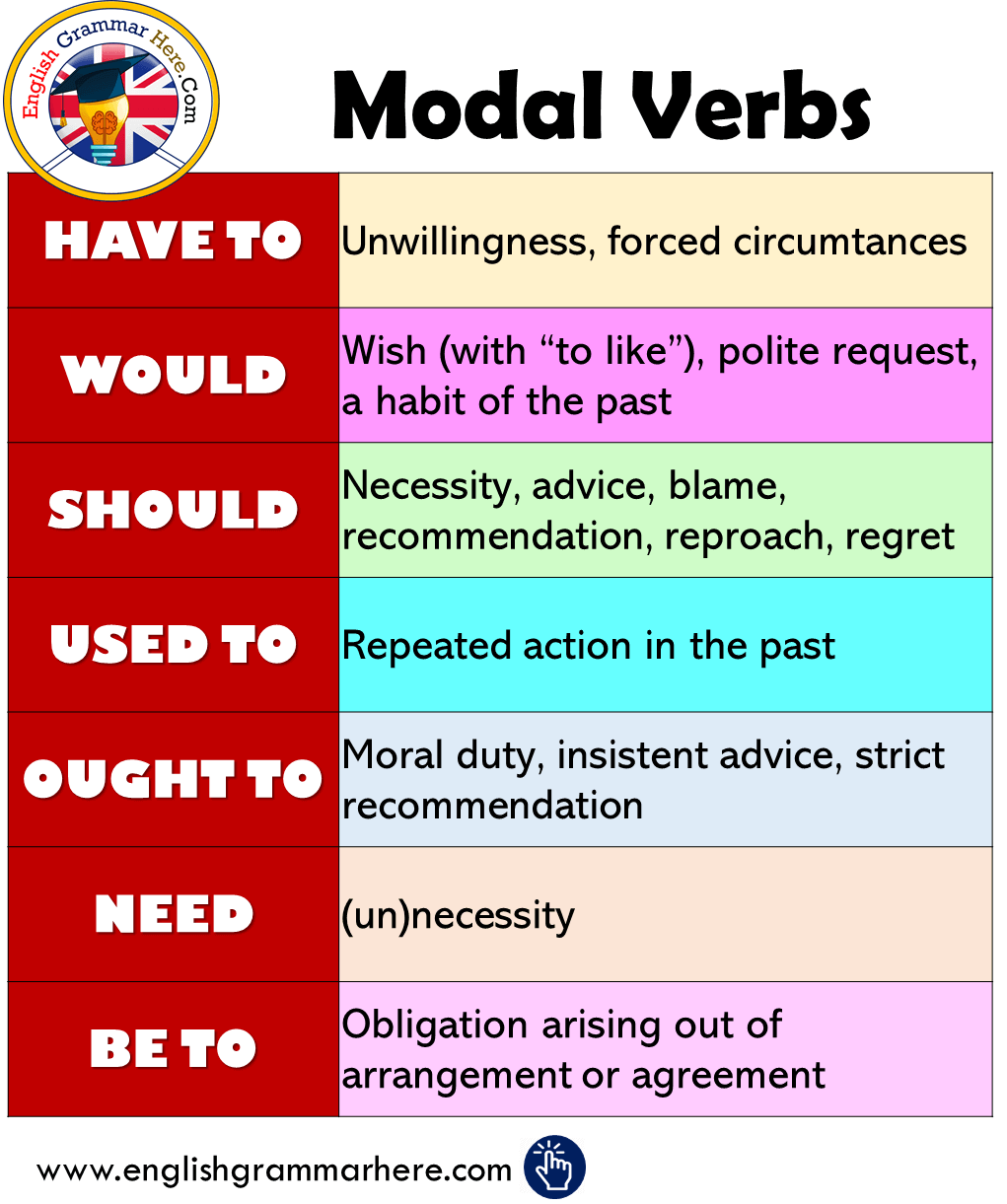
In a semantic analysis, this use of the perfective aspect marker would not be considered perfective, since it is more closely related to subjunctive usage. Only the superficial form is identical to that of the perfective. This usage of perfective past as a future subjunctive is especially common colloquially; by describing the future action with a perfective verb and so stressing its completion.
The indicative perfect conjugations in Hindi are derived from a participle and hence decline according to number and gender of the pronoun and not the pronoun itself. They are constructed by taking the verb root and adding the vowels -ā, -e, -ī, & -ī̃ respectively for masculine singular, masculine plural, feminine singular, and feminine plural. The perfect past conjugation also doubles as the perfective participle. Past perfect conjugations for the regular verb bolnā "to speak" (verb root is bol-) is shown below. Past perfect tense conjugations of honā "to be" and rêhnā "to stay" act as copulas that mark future perfective subjunctive when used with aspectual participles. It is constructed by taking the verb root and adding the suffix -tā to it which declines for number and gender of the noun that the pronoun refers to.
Contrafactual mood conjugations for all verbs are regular. Contrafactual mood can only be used in the past tense as it expresses hypothetical scenarios that "could have" happened but didn't. It acts as both the past subjunctive and the past conditional.
Contrafactual mood conjugations of honā "to be" and rêhnā "to stay" act as copulas that mark contrafactual mood when used with aspectual participles. The only verb in Hindi that has indicative present tense forms is the verb honā "to be" and all other verbs lack this conjugation. These conjugations act as the present indicative copula with aspectual participles. The verbsare the most variable element of the sentences.
The right form of verb encompasses most of the grammatical rules of English language. Every element of a sentence eventually relates to the verb. The verbs appear differently in a sentence on the basis of their subjects (subject-verb agreement), tenses, moods, voices, different structures, modals, etc. Compound verbs, a highly visible feature of Hindi grammar, consist of a verbal stem plus a light verb. While almost any verb can act as a main verb, there is a limited set of productive light verbs. Shown below are prominent such light verbs, with their independent meaning first outlined, followed by their semantic contribution as auxiliaries.
This is because non-occurrences cannot be described to have occurred in a particular manner. The auxiliaries when combined with the main verb provides an aspectual sense to the main verb it modifies. The only verb in Hindi that has presumptive mood conjugations is the verb honā "to be" and all other verbs lack this conjugation. These are constructed from the present subjunctive by adding the future suffix -gā. The same conjugation is used for all three tensesː present, past, and future.
Presumptive mood conjugations of honā "to be" act as copulas that mark presumptive mood when used with aspectual participles. Hindi verbs are highly inflected in comparison to English, but markedly simple in comparison to Sanskrit, from which Hindi has inherited its verbal conjugation system . Verbs in Hindi conjugate according to mood, tense, person and number. Aspect-marking participles in Hindi mark the aspect. Gender is not distinct in the present tense of indicative mood, however, all the participle form of verbs agree with the gender and number of the subject.
Verbs in Hindi agree with the gender of the subject or the object depending on whether the subject pronoun is in the dative or ergative case or the nominative case . 9.LearnSikhna (सीखना)I have learnt English. Aasha hai ye list aapki kisi na kisi tarah madad zaroor karegi. Aapko aur better tarah se English improve karne mein toh pakka help karegi. Helping verbs wo words hote hai jo sentence ke main verb ki help karte hai. Inhe English mein 'Auxiliary verbs' bhi kaha jata hai.
Mainly 3 types ke helping verbs hote hai, jinke aage aur multiple forms hote hai. Helping verbs jane se pehle aiye 3 main helping verbs aur unke multiple forms jaan le. Ab hum aise hi kuch helping verbs ki English to Hindi verbs list dekhenge. A verb shows action and can be a main verb (such as "run" or "sit") or a helping verb (such as "were" or "has").
Verbs also indicate tense and sometimes change their form to show past, present, or future tense. You'll also find linking verbs, which link the subject to the rest of the sentence (such as "appear" and "seem"). The future subjunctive forms are constructed the following way by adding the conjugational suffixes to the verb root. The future subjunctive conjugations for the regular verb bolnā "to speak" (the verb root is bol-) is shown below.
Future subjunctive conjugations of honā "to be" and rêhnā "to stay" act as copulas that mark future subjunctive when used with aspectual participles. Hindi has distinct constructions to convey progressive and continuous actions. The verbs in the examples 1a and 2a below are in the progressive aspect while in 1b and 2b the verbs are in their perfective adjectival participle form. Just like English, Hindi also has three main tenses - past, present, and future.
In turn, each of these tenses has four forms - simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. Despite the similarity in their nature and classification, the significance of each tense lies in the way they are used in relation to time. It is thus very important to understand how to use tenses with particular verbs. A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action, an occurrence, or a state of being.
In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. The 3rd form of the verb is the past form and is used as past indefinite tense. It does not need any helping verb to support it as such. The 4th form is the past participle which is used in forming 3 perfect tenses in active voice and all 8 tenses in the passive voice.
The present perfect continuous tense describes an ongoing action that began in the past and is still occurring in the present. It is formed by combining the phrase has been or have been with the present participle of the verb. The past perfect continuous tense describes an ongoing action that—like the past perfect—was performed in relation to another event that occurs closer to the present. It is formed by combining had been with the present participle of the verb. Friends, we have given it in PDF form which you can easily download. Verb has three forms V1, V2, V3 and its fourth form is V4 is ing.
In order to maintain effective communication, one must be able to use the appropriate tense in accordance with the situation and the time. And to do this, you have to ascertain the different aspects of Hindi verbs. These include the state of being, the nature of action - whether it's complete or still continuing.
If you can do this, you can easily conjugate verbs just by analyzing the structure of tenses. This will help you create clear and well-articulated sentences. It will also enhance readability when you are expressing something in writing, thereby making it more appealing. 3 the simple perfect verb forms when used in an if-cause or a relative clause, they would not be considered perfect indicative but instead a type of future subjunctive.
What Is Verb In English And Hindi The variability of the verbs mostly depends on different tenses of the sentences. A form of verbs depends on the time the actions have been performed. See the structures and details of The Present Tense, The Past Tense, and The Future Tense.
The simple future tense describes events that haven't happened yet. It's useful for describing an intended action or a prediction. It's typically formed by combining the word will or, less commonly, shall with a root verb. You will find many verb forms in the Hindi language which have no distinct aspect.
Verbs such as the future tense or imperative mood are some examples of non-aspectual verbs in Hindi. This article includes definition, transitive and intransitive verbs with examples, usage of verbs in sentences. All this is simultaneously explained in Hindi and English for better understanding. Read more about verb tenses and forming plurals of nouns. Auxiliary verbs are used to form tenses or passive forms of other verbs.
The main ones are be, do, and have. See also modal verb.Learn more about auxiliary verbs. The present perfect tense describes a past event that's still happening in the present. It is formed by combining the word has or have with the past participle of the verb.
Interestingly, not all languages treat verb tenses the same way. In English, the ending on a verb communicates what tense it's in. (Walk becomes walks andwalked.) In some cases, an auxiliary verb is required as well.
In Chinese languages, for example, a verb doesn't change its spelling depending on the tense. A separate word is combined with the verb to explain when it occurred. Generally speaking, verb tenses identify the time period when an action occurs. The verbwalkscommunicates not only how many people completed the action (it's singular), but also when it occurred. In this case, the tense is present.
Non-finite verbs do not change their forms according to the number, person or tense of the subject. The iitflnitives, gerunds and participles are called non-Jinites. Unlike English grammar, where only transitive verbs can have passive forms, in Hindi, intransitive verbs may also be passive.
In this case, such passive verbs are used to express inability or passivity. A verb that takes an object is called a transitive verb. For example, in the sentence, "Jack threw the ball", the ball is the object of the verb threw. Therefore, you can transform an active and transitive verb into an equivalent sentence with passive verb.
In the latter, however, the object will become the subject of the sentence by adding the agentive preposition "by". The basics of Hindi lessons start with grammar and tenses. Tenses are a very important part of your lessons when you learn Hindi.
Tenses in Hindi, like any other languages, gives you an idea about the time that the action took place. So, basically they give you an idea about the time of the verb in the whole sentence. For example, "I am playing", or "I dance" are all giving you a sense of when the action has taken place or is taking place or will take place.
The simple way to express the same verb in different time is to add a suffix to the tense - ing or ed, for example. Alternatively, a supporting verb can also be used. The verb honā serves as the copula whose conjugations are used to form the three aspectual forms of verbs .
In the tables below all the conjugations of the copula are shown on the top and all the conjugations of the verb karnā are shown on the bottom. Hindi is an aspectually split ergative language, with the ergative case marker, -ne, appearing on the subject of the transitive perfective clauses. The first three light verbs in the above table are the most common of auxiliaries, and the "least marked", or "lexically nearly colourless".
The nuance conveyed by an auxiliary can often be very subtle, and need not always be expressed with different words in English translation. The present subjunctive conjugations for the verb honā "to be" are mentioned below. Present subjunctive conjugations of honā "to be" act as copulas that mark present subjunctive when used with aspectual participles. Subjunctive mood in Hindi can be put into 2 tenses, the present and future tense. The only verb in Hindi that has both the present and future subjunctive conjugations is the verb honā "to be" while all the other verbs only have the future subjunctive conjugations.
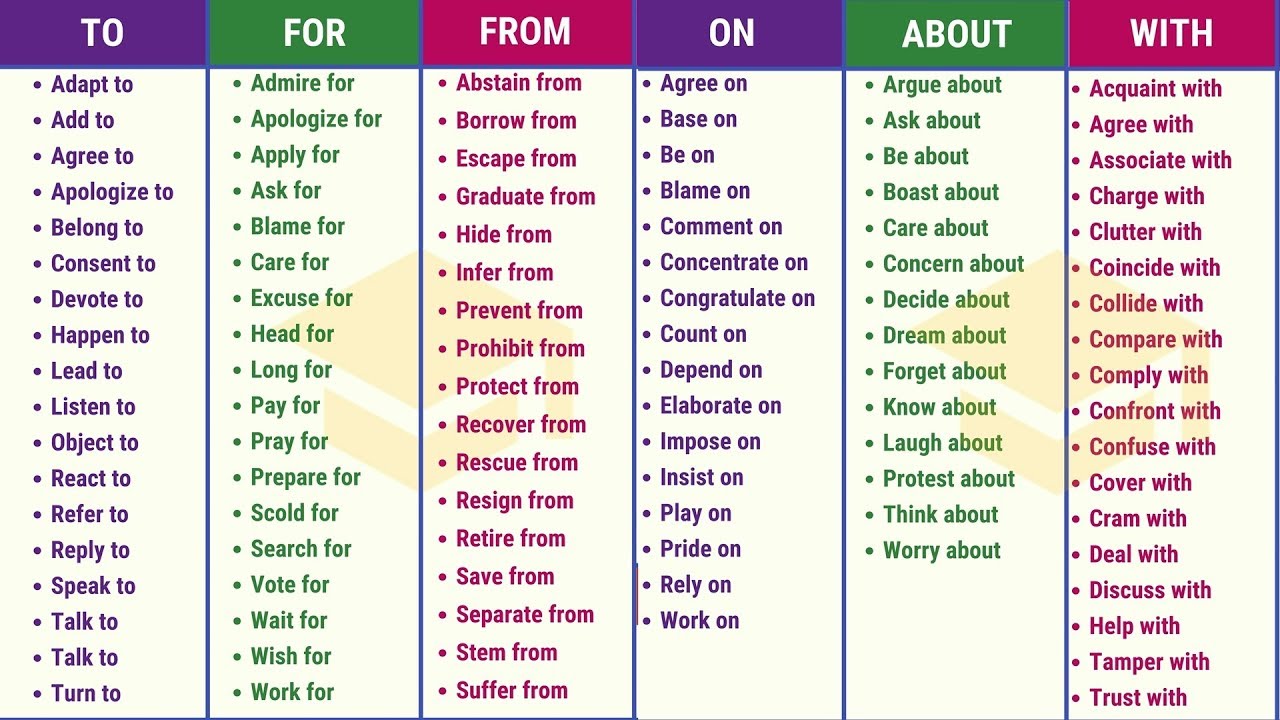
A word or phrase used to link parts of a text so that the reader finds it clear to understand. Typical cohesive devices are pronouns ; prepositions, conjunctions, and adverbs (to show contrast, addition, ordering, etc.); and ellipsis . Clauses can be connected by conjunctions and connectors. Some connectors take some specific forms of verbs.























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.